Python3サンプルコード集(その1)
最近はC言語ばっかりでしたが、今後もソフトウェア屋をやるのであればPythonかRubyは慣れておきたいところ。Pythonを新たに始めるならPython3一択らしい(Python2は必要になったら調べれば事足りるため)。個人的に新しい言語を覚えるときは短いサンプルコードを見て作るのが一番早いので簡単なものからはじめてみた。
目次
Python3のインストール
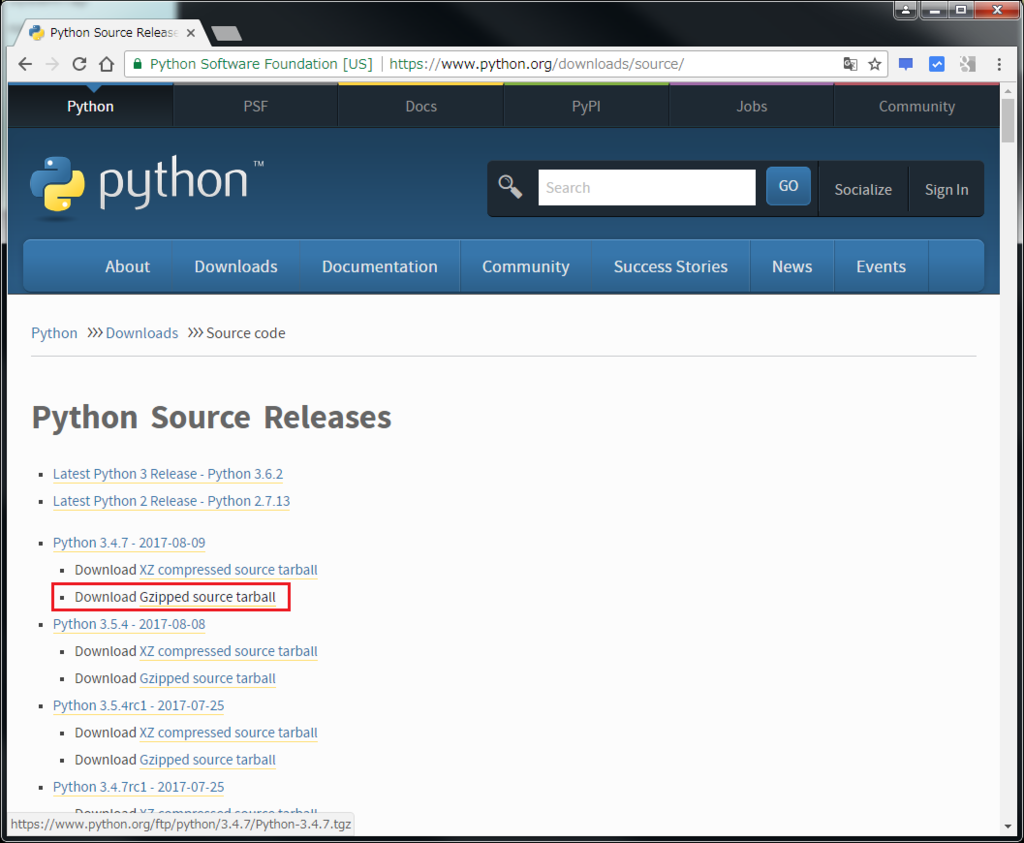
まずはPython3のインストールから。Linux環境(CentOS7)に下記のソースコード(tarball)をダウンロード後、ビルドしてインストールする。
https://www.python.org/downloads/source/
[user@localhost ~]$ sudo yum install zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gcc
[user@localhost Download]$ wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.4.7/Python-3.4.7.tgz
[user@localhost Download]]$ tar zxvf Python-3.4.7.tgz
[user@localhost Python-3.4.7]$ cd Python-3.4.7
[user@localhost Python-3.4.7]$ ./configure
[user@localhost Python-3.4.7]$ make
[user@localhost Python-3.4.7]$ sudo make install
[user@localhost Python-3.4.7]$ sudo ln -s /usr/local/python/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/python
[user@localhost Python-3.4.7]$ sudo ln -s /usr/local/python/bin/pip3.4 /usr/local/bin/pip
[user@localhost ~]$ python --version
Python 3.4.7インストール後にpythonのバージョンを確認して一致していればOK。
サンプル集
Hello Worldその1
#!/usr/local/python
print("hello world")[user@localhost basic]$ python hello1.py
hello worldHello Worldその2
#!/usr/local/python
import sys
sys.stdout.write("hello world\n")[user@localhost basic]$ python hello2.py
hello worldprintで改行しない
#!/usr/local/python
print("hello world", end="")[user@localhost basic]$ python nokaigyo.py
hello world[user@localhost basic]$各種演算
#!/usr/local/python
print('2+1 =', 2+1)
print('10-3 =', 10-3)
print('7*4 =', 7*4)
print('5/2 =', 5/2)
print('5//2 =', 5//2)
print('10%3 =', 10%3)
print('2**10 =', 2**10)[user@localhost basic]$ python ensan.py
2+1 = 3
10-3 = 7
7*4 = 28
5/2 = 2.5
5//2 = 2
10%3 = 1
2**10 = 1024九九表
#!/usr/local/bin/python
for x in range(0,9):
for y in range(0,9):
print('{0}'.format('%2d ' % ((x+1) * (y+1))), end="")
print('')[user@localhost basic]$ python 99.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27
4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54
7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63
8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72
9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81円周率を求める
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import sys
import math
#
# Machin's formula
# π/4 = 4 * Arctan(1/5) - Arrctan(1/239)
#
def arctan(x, k):
arctanx = 0
for n in range(0, k):
arctanx += pow(-1, n) * (1/(2 * (n+1) - 1)) * pow(x, (2*(n+1) - 1))
return arctanx
if __name__ == '__main__':
argv = sys.argv
if len(argv) != 2:
print('usage : {0} <n>'.format(argv[0]))
quit()
for k in range(1, int(argv[1])):
pi = 4 * (4 * arctan(1/5, k) - arctan(1/239, k))
print(pi)[user@localhost basic]$ python pi.py 10
3.141592653589836hexdumpコマンド風
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import sys
if __name__ == '__main__':
argv = sys.argv
if len(argv) != 2:
print('usage : {0} <file>'.format(argv[0]))
quit()
f = open(argv[1], 'rb')
dat = f.read()
for i in range(len(dat)):
# 文字表示と改行
if (i >= 1 and i % 16 == 0):
print('|', end="");
for n in range(16):
if (0x20 <= int(dat[i+n-16]) and int(dat[i+n-16]) <= 0x7e):
print('%c' % dat[i+n-16], end="")
else:
print('.', end="")
print('|');
# オフセット表示
if (i == 0 or i % 16 == 0):
print('%08x ' % i, end='')
# 16進数表示
print('%02x ' % dat[i], end='')
# 8byteで空白区切り
if (i >= 1 and (i+1) % 8 == 0):
print(' ', end="")
# 最後に改行
print('')
f.close[user@localhost basic]$ hexdump -C Windows_Error.wav |head
00000000 52 49 46 46 24 9e 02 00 57 41 56 45 66 6d 74 20 |RIFF$...WAVEfmt |
00000010 10 00 00 00 01 00 02 00 44 ac 00 00 10 b1 02 00 |........D.......|
00000020 04 00 10 00 64 61 74 61 00 9e 02 00 00 00 00 00 |....data........|
00000030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
[user@localhost basic]$ python file.py Windows_Error.wav > test.txt
[user@localhost basic]$ head test.txt
00000000 52 49 46 46 24 9e 02 00 57 41 56 45 66 6d 74 20 |RIFF$...WAVEfmt |
00000010 10 00 00 00 01 00 02 00 44 ac 00 00 10 b1 02 00 |........D.......|
00000020 04 00 10 00 64 61 74 61 00 9e 02 00 00 00 00 00 |....data........|
00000030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|Unixドメインソケット
サーバ側
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import os
import sys
import socket
class UnixDomainServer:
def __init__(self, socket_path):
self.socket_path = socket_path
def start(self):
s = self.socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_UNIX, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.bind(self.socket_path)
s.listen(1)
try:
while True:
sys.stdout.write("wait connection\n")
connection, address = s.accept()
sys.stdout.write("connected\n")
self.accepted(connection, address)
sys.stdout.write("disconnect\n")
finally:
os.remove(self.socket_path)
def accepted(self, connection, address):
data = connection.recv(1024)
sys.stdout.write("receive from client: {}\n".format(data.decode()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
server = UnixDomainServer('./ud.sock')
server.start()クライアント側
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import sys
import socket
class UnixDomainClient:
def __init__(self, socket_path):
self.socket_path = socket_path
def start(self):
s = self.socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_UNIX, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(self.socket_path)
def send(self):
message = "Hello"
sys.stdout.write("send message to server : {0}\n".format(message))
self.socket.send(message.encode())
def close(self):
self.socket.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
client = UnixDomainClient('./ud.sock')
client.start()
client.send()
client.close()[user@localhost basic]$ python unix_sever.py
wait connection
connected
receive from client: Hello
disconnect
wait connection
[user@localhost basic]$ python unix_client.py
send message to server : Hello今は全くまとまりが無いですが、サンプルが増えたら整理できればと思います。
コアダンプの数だけ強くなれるよ –
Python3サンプルコード集(その2) – コアダンプの数だけ強くなれるよ
Pythonのサンプルコードです。ネットワーク系が中心となります。書かなくなるとすぐ忘れてしまうので備忘録とし


コメント